The Global Octane Shortage and its impact on Aromatics

What is Octane and why does it matter to aromatics?
The past year has seen unprecedented disruptions to gasoline and octane markets across the globe. The rippling and lasting effects of COVID-19 lockdowns and restrictions have impacted industries and consumer demand in sometimes unpredictable ways. Aromatics products have long been used in gasoline blending to enhance properties in fuels, but this has sometimes been a secondary focus to chemical demand routes. The unusual events post-COVID-19 have shifted aromatics for use as octane into the spotlight.
Gasoline blending is a balance between optimizing costs and meeting legislated quality specifications. When considering aromatics for octane, the most important element is the octane number, which is a measure of the pressure a fuel can withstand before ignition. This is aimed at preventing engine ‘knocking’, which is the misfiring of pistons in the engine at a non-optimal point in their stroke. Knocking decreases the efficiency of engines and increases the wear, so it is important to minimize it. The octane of a chemical is compared to heptane and (0) and isooctane (100) and given a value. There are two methods that are used: Research Octane Number (RON), Motor Octane Number (MON), and the average of the two the Anti-knock Index (AKI or Pump Octane Number (PON)).
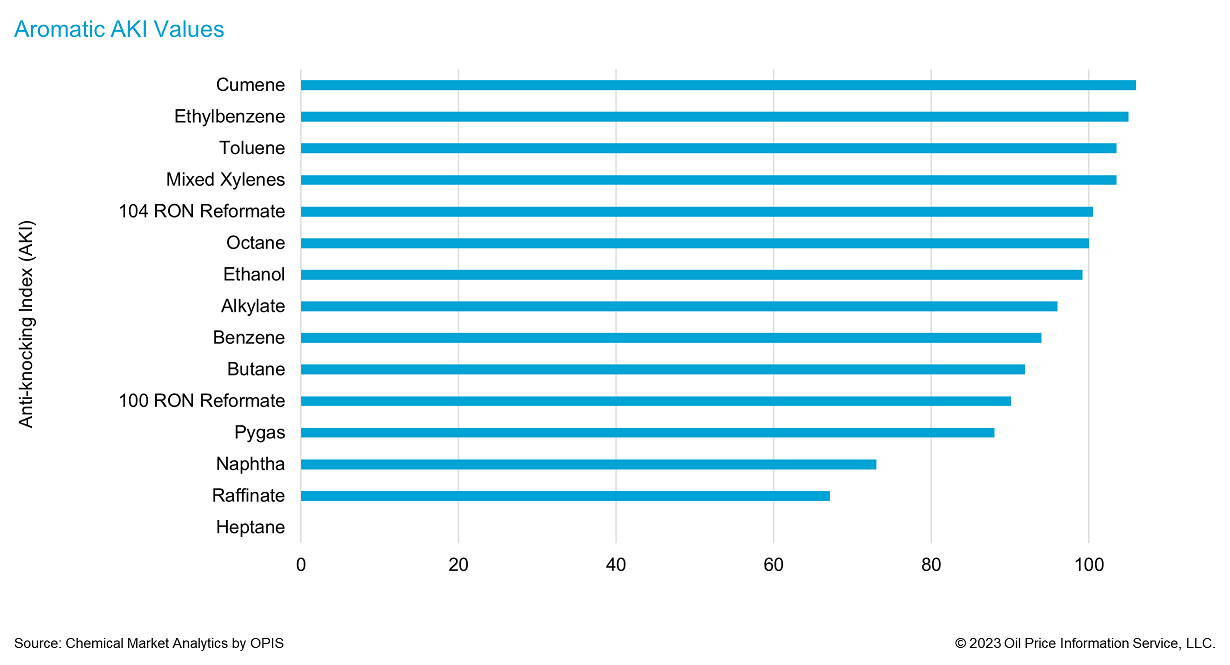
Unfinished or straight-run gasoline has an octane number of around 70, regular gasoline has an octane value of 87 AKI or RON 91 whereas premium gasoline has an AKI of 91 or RON of 95. For octane values to meet the required specification, higher octane components must be added to gasoline blends to increase the overall octane rating. Common octane-boosting blend components are aromatics such as reformate (RON 97 to 104) or toluene (RON 121), alkylates (RON 94-98), and alcohols; primarily ethanol (108.6 RON).
A gasoline producer or blender may buy octane components from the market to facilitate on-specification gasoline. This need is enhanced when blenders use a low-octane blend stock such as light naphtha and thus require a greater proportion of high-octane components to meet specification requirements.
Adding to the complex world of gasoline blending, aromatic content in finished gasoline is limited to 35%, with benzene limits far lower. Because of this, the excess benzene in the reformate must be extracted prior to the reformate stream being added to gasoline blends.
Gasoline and the Summer of 2022
In the summer of 2022 gasoline demand was higher than anticipated and this led to a large and unexpected spike in octane demand.
Several factors in concert contributed to the unprecedented gasoline market in 2022. Refinery rationalization between early 2020 and the summer of 2022 saw over 14% of global refining capacity lost. US gasoline stocks were also much lower than at any point in the previous five years as producers chose to hold lower inventories after two successive years of being caught with much higher stocks than were justified by demand. Finally, the outbreak of the Russia-Ukraine conflict saw supply disruptions of crude oil and petroleum products out of Russia, tightening supply in other regions.
The eradication of almost all COVID restrictions in 2022 saw increased consumer demand – especially in the travel sector. This tightened the market leading to gasoline and octane prices rising far above historical norms.
Chemicals or Gasoline
Reformate can be directly blended into gasoline or can be used as a petrochemical feedstock for the extraction of benzene, toluene, and mixed xylenes (BTX). As such the price of reformate for octane acts as a price floor, but its value may be higher if the value of the constituent chemicals minus extraction costs is higher than this blended value. If chemical demand and prices are strong enough BTX will be extracted from reformate to maximize margins.
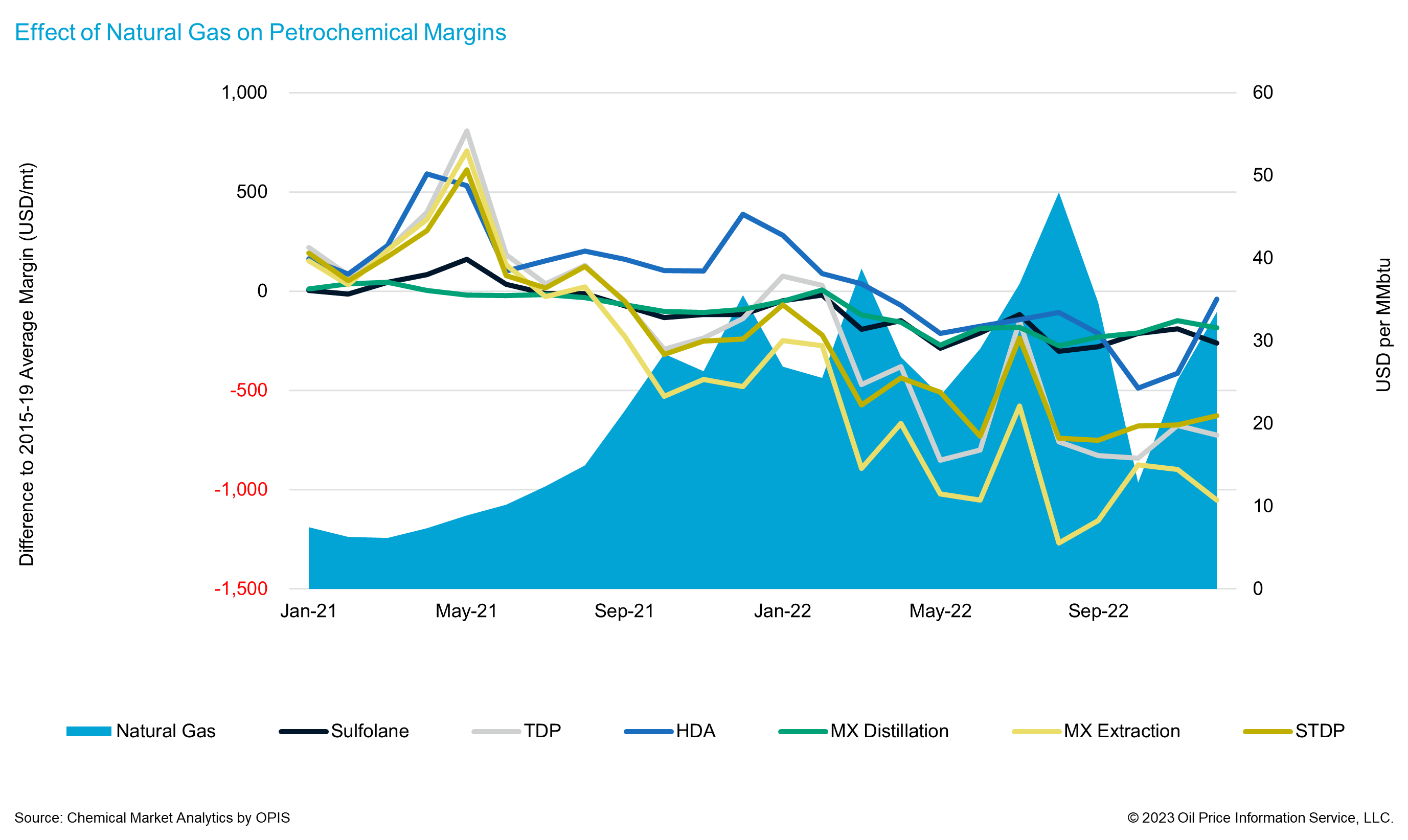
2022 saw a two-fronted attack on the chemical sector as the rise in gasoline prices was matched by a meteoric rise in the price of natural gas in Europe to €339 per MWh in August 2022 (over 10 times the 2019 average). This brought a huge increase in variable costs for chemical producers, as prices could not keep pace with costs, and negative margins inevitably followed. Aromatics extraction was minimized wherever possible, and retention of aromatics in the gasoline pool was favored. The combination of higher costs and rising blend values meant the price of European aromatics rose substantially in the summer of 2022 with prices for high-octane aromatics more than doubling versus the same month in 2021.
Looking Ahead
With low levels of growth forecast for Europe in 2023 and limited refinery capacity increases until 2024, the 2023 summer driving season is anticipated to be similar to 2022, with an expectation of gasoline and octane shortages. With chemicals demand expected to be depressed globally for the first half of 2023, it is likely that once again alternative octane components will move into the blending pool if the gasoline market can outcompete weak chemical markets.
Sanctions on Russian oil products came into effect in February, and this is expected to have an influence on naphtha, with two contrasting effects. Firstly, the ban on Russian naphtha imports will be decreasing the availability of naphtha in Europe. This is already increasing the price of naphtha compared to gasoline, but it should also decrease the availability of cheap low-RVP, low-octane blend components – such as light naphtha – which would also reduce the ability of blenders to pay higher prices for high-octane components.
Secondly, the ban will decrease the availability of heavy naphtha (which made up large amounts of Russian imports), decreasing the external feedstock for reformers. This could limit the operating rate of reformers and decrease the volume of high-octane blend components available to the market. This should push up the premia of blend components due to lower availability.
Further complicating the global gasoline balance is the ongoing recovery of mainland China. Mainland Chinese domestic demand recovery through 2023 is anticipated to be challenging and refined product export quotas have been high to assist gasoline producers in the country. If mainland China can recover faster than expected this will add pressure on global gasoline and octane markets as trade flows change as exports from mainland China decrease.
Merchant market prices for chemicals chains must therefore be capable of covering high feedstock costs and increased extraction costs or there will be no incentive for producers to operate beyond minimum levels. It is likely that for aromatics products where there is alternative use as a blend component, 2023 will again see octane and blend values at levels that make premia required for extraction economically unfeasible for the European industry.
Chemical Market Analytics expects that there may be substantial disruptions to aromatics markets in 2023. The expected strength of octane in 2023 is likely to maintain the disruption in the aromatics value chains in both Europe and the US this summer if the expectation of a worldwide octane shortage and a tight octane market becomes a reality.
Authors
David Potter Matthew Hamilton
Aromatics and Fibers, EMEA
Aromatics and Fibers, EMEA

Megan Brenchley
Aromatics and Fibers, EMEA
Embracing the Infinite Possibilities
Chemical Market Analytics by OPIS, a Dow Jones company, with participation from The Wall Street Journal, Barron’s, and Factiva, presents the 2023 World Chemical Forum, a new event that redefines comprehensive exploration of the future of chemicals and energy, their inter-relationships, and how both markets will address global challenges this century.
Energy and chemical markets are evolving in profound ways and ushering in a fourth historical industrial and social revolution with Infinite Possibilities. Leading global experts and industry executives from all market sectors will convene to hear expert forecasts for key chemical and energy markets and discuss pivotal initiatives including chemical sustainability, the evolving logistics landscape, risk management strategies, and the future impact of Asia on the world.
The comprehensive agenda includes one day dedicated to a global view of the current and future chemical market and two days of guidance on the specific trends shaping the market.
Don’t miss any of it: register now and ensure your attendance at this exciting inaugural event!
Learn how we can help you prepare and navigate market disruptions
