2024 Polyolefins Outlook

2023 – a Year of Unprecedented Low Margins
2023 was a challenging year for both producers and converters in Asia. Most of the producers in Asia utilize naphtha as a feedstock, and the cost of production was high as naphtha prices remained high.
However, polyolefin prices were depressed because of an oversupply situation plaguing the industry and weak end-use demand. Soft demand was prevalent throughout the year with occasional restocking activities which did not manage to support prices at a much higher level. This was attributable to the uncertainty in the macro-economic environment, further exacerbated by geopolitical issues.
Producers in Asia continued to grapple with low margins for most of the year, while inflation coupled with higher interest rates through the year dampened consumer spending, which in turn impacted demand for polyolefins.
2024 – the Year of the Dragon Continues to Be Fraught With Challenges
In 2024, the outlook is forecast to remain weak, but cautiously optimistic. Both global GDP (Gross Domestic Product) growth and headline inflation are expected to decline. This is also likely to motivate Central Banks worldwide to reduce interest rates and thus spur consumer demand. In mainland China, the largest demand market for polyolefins, the country’s central bank has pledged to give support for a steady economic growth. However, the growth rate is expected to be slow and fraught with challenges.
The volatility from geopolitical tensions is expected to continue in 2024. The conflict between Russia and Ukraine has been ongoing, which has caused uncertainty in the economic outlook. Inflation has dampened demand in the European region. Currently, tensions in the Red Sea area have resulted in higher logistical costs for certain routes. The impact on the polyolefin market from geopolitical tensions remains significant, even if it is not directly influenced. Natural factors such as the drought in the Panama Canal has also increased shipment time for vessels using that route. Thus, the polyolefins market can be impacted by geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, or disruptions in the supply chain which are unpredictable.
Supply Continues to Be Ample in 2024
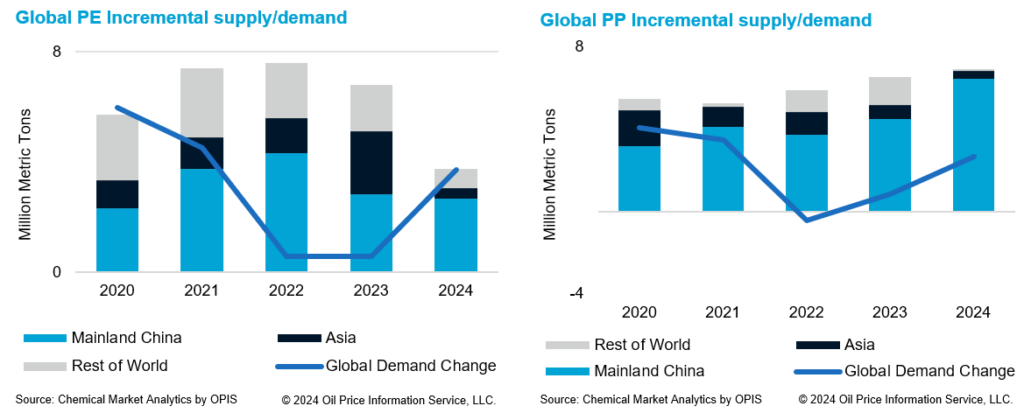
2024 is expected to be a year where the oversupply situation continues to persist. For PE, although incremental supply is similar to incremental demand, the excess incremental supply of 16 million metric tons from the past 3 years is expected to continue to weigh on the market. Total new PE capacity in 2024, excluding the incremental capacities from 2023 accounts for 4.3 million metric tons. All these capacities are starting up in mainland China. These capacities are predominantly naphtha-based, with small volumes from mixed feed and coal-based crackers. Operating rates of naphtha-based producers are expected to be lower because of the higher cost of production.
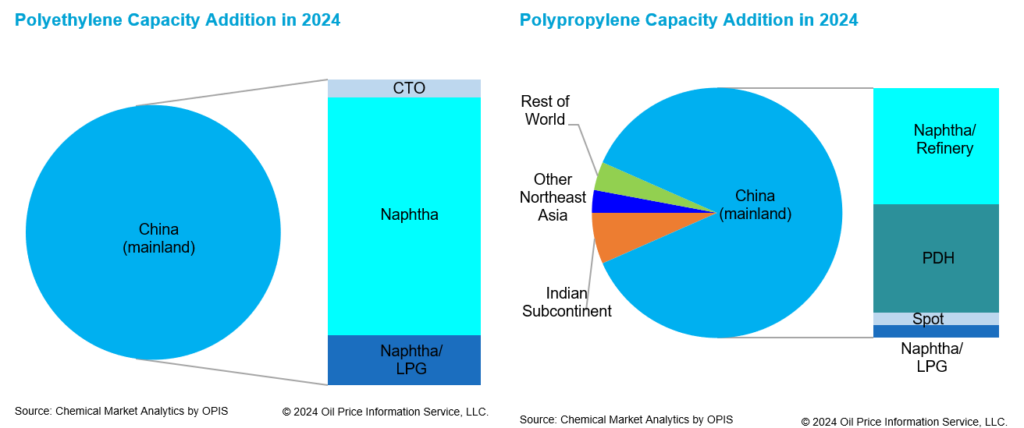
For PP, there has been excess incremental supply over incremental demand since 2020. In 2024, the excess incremental supply is expected to be at 7 million metric tons, bringing the cumulative excess supply beyond demand growth to 19 million metric tons since 2020. Total new PP capacity in 2024, excluding the incremental capacities from 2023 is expected to be at 6.8 million metric tons. Capacity addition is driven by mainland China.
The feedstock for PP plants is more diversified, with feedstock routes such as naphtha, PDH (propane dehydrogenation), mixed feed and spot propylene. Operating rates are likely to be depressed with so many new plants coming up in Asia.
Asia Expected to Drive Demand Growth
While most of the capacity growth comes from Asia, demand growth is more spread across globally. In 2023, PE incremental demand was negative for markets outside of Asia. This is despite a much lower growth of 2.5% in mainland China last year, indicative of a challenging operating environment Asia is expected to lead the recovery, accounting for a sizable portion of the incremental global PE demand, with mainland China and India leading this growth.
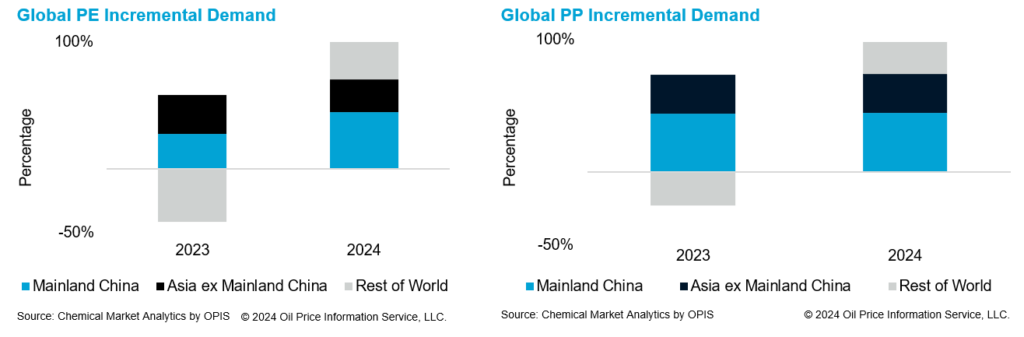
The situation is similar for PP. In 2023, demand growth in mainland China was 2.2% and accounted for about 60% of Asia’s demand growth.
In 2024, global PP demand growth is expected to improve from the level seen in 2023. Asia is expected to lead the global incremental demand growth. PP demand for automotive applications is expected to be healthy as mainland China overtook Japan as the world top automobile exporter last year and this momentum is expected to continue.
Polymer-naphtha Spreads Are Expected to Remain Low
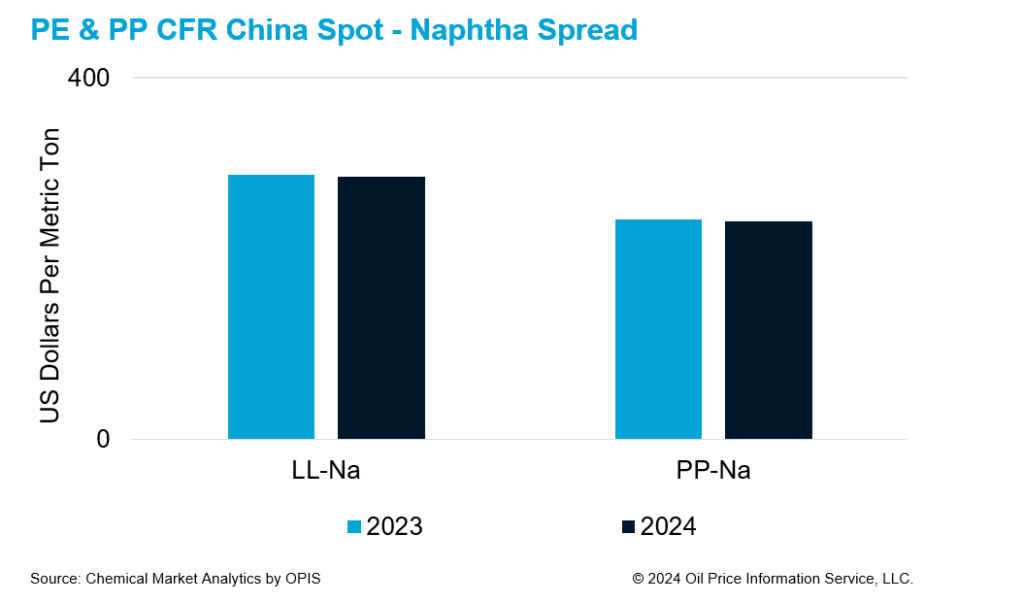
With a weak outlook in 2024, demand is not expected to pick up significantly, which would limit the uptick on polyolefins prices. This may result in depressed margins, and producers are likely to continue operating at lower rates to minimize losses. Despite low operating rates in Asia, supplies will be ample from low-cost suppliers in the Middle East and North America. With ample supply and a soft demand outlook, naphtha-polymer spreads are likely to be range bound at 2023 levels.
Overall, PE-naphtha spread is expected to be low, thus keeping producers’ margins below breakeven level. PP-naphtha spread is expected to be lower than PE-naphtha spread because of significant new supplies coming up, especially in mainland China. Thus, even as demand growth is expected to be better, ample supplies will weigh on the polymer-naphtha spreads.
Conclusion
The outlook for the polyolefins market in 2024 is not expected to be very robust, with the oversupply situation weighing on the market. Demand growth is expected to be better than that of 2023 but is unlikely to be significantly higher because of headwinds in the macro-economic environment.
Geopolitical tensions will continue to impact the polyolefins market in indirect ways, while any issue impacting the supply chain will support polyolefin prices at higher levels. 2024 will continue to be challenging for producers as they are expected to continue to suffer from lower margins since end-use demand is expected to be weak while supplies remain ample.
In such a challenging business environment, several naphtha-based polyolefins company management will have to critically evaluate their strategic outlook and consider partial or complete shutdown of their production facilities which are making cash losses.
Author

Yi Ling Tan
Director, Southeast Asia Polyolefins
Learn how we can help you prepare and navigate market disruptions today.

